model.py 會透過 DBiRNN class 來建構 CTC 模型,前一天中提到過我們是使用 LSTM 架構,也可以根據參數選擇使用基本的 RNN 架構 或是 GRU 架構。
build_multi_dynamic_brnn() function 就是在建立3層的雙向 LSTM ,模型當中會加入 dropout 丟棄部分的神經元以避免模型在訓練過程中 overfitting (根據 keep_prob 決定丟棄的比率)。
建立完 3 層的雙向 LSTM 後面接著就是一層的 fully-connected 然後再經過 CTC (tf.nn.ctc_loss)計算得到輸出序列。
# model.py
import argparse
import time
import datetime
import os
from six.moves import cPickle
from functools import wraps
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.rnn.python.ops import *
from tensorflow.python.ops.rnn import bidirectional_dynamic_rnn
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
def dropout(x, keep_prob, is_training):
return tf.contrib.layers.dropout(x, keep_prob=keep_prob, is_training=is_training)
def build_multi_dynamic_brnn(args,
maxTimeSteps,
inputX,
cell_fn,
seqLengths,
time_major=True):
hid_input = inputX
for i in range(args.num_layer):
scope = 'DBRNN_' + str(i + 1)
forward_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(args.num_hidden, forget_bias=1.0)
backward_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(args.num_hidden, forget_bias=1.0)
# tensor of shape: [max_timestamp, batch_size, input_size]
outputs, output_states = bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(forward_cell, backward_cell,
inputs=hid_input,
dtype=tf.float32,
sequence_length=seqLengths,
time_major=True,
scope=scope)
# forward output, backward ouput
output_fw, output_bw = output
# hidden state
hidden = output_fw + output_bw
# use dropout
hidden = dropout(hidden, args.keep_prob, (args.mode == 'train'))
if i != args.num_layer - 1:
hid_input = hidden
else:
outputXrs = tf.reshape(hidden, [-1, args.num_hidden])
output_list = tf.split(outputXrs, maxTimeSteps, 0)
fbHrs = [tf.reshape(t, [args.batch_size, args.num_hidden]) for t in output_list]
return fbHrs
class DBiRNN(object):
def __init__(self, args, maxTimeSteps):
self.args = args
self.maxTimeSteps = maxTimeSteps
if args.layerNormalization is True:
if args.rnncell == 'rnn':
self.cell_fn = lnBasicRNNCell
elif args.rnncell == 'gru':
self.cell_fn = lnGRUCell
elif args.rnncell == 'lstm':
self.cell_fn = lnBasicLSTMCell
else:
raise Exception("rnncell type not supported: {}".format(args.rnncell))
else:
if args.rnncell == 'rnn':
self.cell_fn = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell
elif args.rnncell == 'gru':
self.cell_fn = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell
elif args.rnncell == 'lstm':
self.cell_fn = tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell
else:
raise Exception("rnncell type not supported: {}".format(args.rnncell))
self.build_graph(args, maxTimeSteps)
def build_graph(self, args, maxTimeSteps):
self.graph = tf.Graph()
with self.graph.as_default():
self.inputX = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(maxTimeSteps, args.batch_size, args.num_feature)) # [maxL,16,39]
inputXrs = tf.reshape(self.inputX, [-1, args.num_feature])
self.targetIxs = tf.placeholder(tf.int64)
self.targetVals = tf.placeholder(tf.int32)
self.targetShape = tf.placeholder(tf.int64)
self.targetY = tf.SparseTensor(self.targetIxs, self.targetVals, self.targetShape)
self.seqLengths = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(args.batch_size))
self.config = {'name': args.model,
'rnncell': self.cell_fn,
'num_layer': args.num_layer,
'num_hidden': args.num_hidden,
'num_class': args.num_class,
'activation': args.activation,
'optimizer': args.optimizer,
'learning rate': args.learning_rate,
'keep prob': args.keep_prob,
'batch size': args.batch_size}
fbHrs = build_multi_dynamic_brnn(self.args, maxTimeSteps, self.inputX, self.cell_fn, self.seqLengths)
# fully connected
with tf.name_scope('fc-layer'):
with tf.variable_scope('fc'):
weightsClasses = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([args.num_hidden, args.num_class]), name='weightsClasses')
biasesClasses = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([args.num_class]), name='biasesClasses')
logits = [tf.matmul(t, weightsClasses) + biasesClasses for t in fbHrs]
logits3d = tf.stack(logits)
self.var_op = tf.global_variables()
self.var_trainable_op = tf.trainable_variables()
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.ctc_loss(self.targetY, logits3d, self.seqLengths))
if args.grad_clip == -1:
# not apply gradient clipping
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(args.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
else:
# apply gradient clipping
grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(self.loss, self.var_trainable_op), args.grad_clip)
opti = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(args.learning_rate)
self.optimizer = opti.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.var_trainable_op))
self.predictions = tf.to_int32(tf.nn.ctc_greedy_decoder(logits3d, self.seqLengths, merge_repeated=True)[0][0])
if args.level == 'cha':
self.errorRate = tf.reduce_sum(tf.edit_distance(self.predictions, self.targetY, normalize=True))
self.initial_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=1, keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=200)
介紹完了除噪模型與辨識模型,完整的模型架構如圖 1: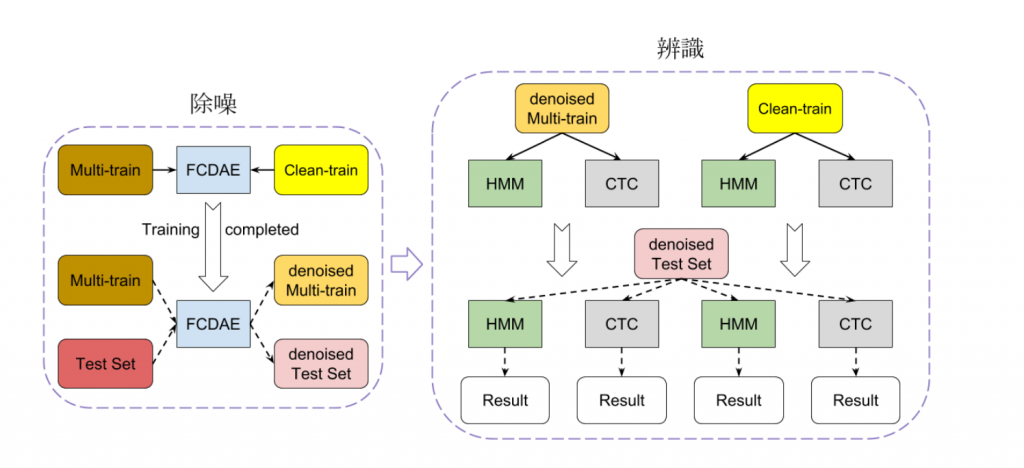
圖 1: 完整模型架構圖
下一篇的文章我們會透過詞正確率(Word Correct Rate) 來評估模型的效能。
